By Iver Van de Zand, SAP
If there is one term that always is food for discussion when I talk to customers, it is definitely “dashboard”. What exactly is a dashboard, how close is it to a storyboard, are dashboard only on summarized data and when to use a dashboard versus a storyboard. Tons of questions that already start in a bad shape because people have other perceptions of what a dashboard really is. And let’s be honest; take a canvas, put a few pies on it and a bar-chart, and people will already mention it as a dashboard. Let’s see whether we can fine-tune this discussion a bit.
A Dashboard
A business intelligence dashboard is a data visualization technique that displays the current status and/or historical trends of metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) for an enterprise. Dashboards consolidate and arrange numbers, metrics and sometimes performance scorecards on a single screen. They may be tailored for a specific role and display metrics targeted for a single point of view or department. The essential features of a BI dashboard product include a customizable interface and the ability to pull real-time data from multiple sources. The latter is important since lots of people think dashboards are only on summarized data which is absolutely not the case; dashboards consolidate data which may be of the lowest grain available! Key properties of a dashboard are:
-
Simple and communicates easily and straight
-
Minimum distractions, since these could cause confusion
-
Supports organized business with meaning, insights and useful data or information
-
Applies human visual perception to visual presentation of information: colors play a significant role here
-
Limited interactivity: filtering, sorting, what-if scenarios, drill down capabilities and sometimes some self-service features
-
They are often “managed” in a sense that the dashboards are centrally developed by ICT, key users or a competence center, and they are consumed by the end-users
-
Offer connectivity capabilities to other BI components for providing more detail. Often these are reports with are connected via query-parsing to the dashboards
A Storyboard
Is there a big difference between a storyboard and a dashboard? Mwah, not too much: they both focus on communicating key – consolidated – information in a highly visualized and way which ultimately leaves little room for misinterpretation. For both the same key words apply: simple, visual, minimum distraction.
The main difference between a dashboard and a storyboard is that the latter is fully interactive for the end user. The interactivity of the storyboard is reflected through capabilities for the end user to:
-
Sort
-
Filter data: include and exclude data
-
Change chart or graph types on the fly
-
Add new visualizations on the fly; store and share them
-
Drill down
-
Add or adjust calculated measures and dimensions
-
Add new data via wrangling, blending or joining
-
Adjust the full layout of the board
-
Create custom hierarchies or custom groupings
-
Allow for basic data quality improvements (rename, concatenate, upper and lower case etc)
Another big difference between dashboards and storyboards is that storyboards are self-service enabled boards meaning the end user creates them him/herself. Opposite to dashboards that are typically “managed” and as such are created centrally by ICT, key users or a BICC, and are consumed by the end user.
A Dashboard versus a Storyboard
So your question, dear reader, is “what is the day-to-day difference and what to you use when”? Well the answer is in the naming of both boards:
The purpose of a storyboard is to TELL A STORY: the user selects a certain scope of data (which might be blended upon various sources) and builds up a story around that data that provides insights in it from various perspectives. All in a governed way of course. The story is built upon various visualizations that are grouped together on the canvas of the storyboard. These visualizations can be interdependent – filtering on one affects the others – or not. The canvas is further enriched with comments, text, links or dynamic pictures … all with the purpose to complete the story.
Storyboarding has dramatically changed day-to-day business: the statement “your meeting will never be the same” applies definitely. Your meetings are now being prepared by creating a storyboard; meetings are held using storyboards to discuss on topics and make funded decisions, simulations on alternative decisions are done during the meetings using the storyboards and final conclusions can be shared via the storyboards. Governed, funded, based on real-insights!
A dashboard has a pattern of analyzing that is defined upfront. It is about KPI’s or trends of a certain domain, and you as a user consume that information. You can filter, sort or even drill down in the data, but you cannot change the core topic of data. If the KPI’s are on purchasing information, it is on purchasing information and stays like it. You neither can add data to compare it.
In a number of situations one does not want the end user to “interact” with the information since it is corporate fixed data that is shared on a frequent and consistent time. Enterprises want that information to be shared for insights in a consistent, regular and recognizable way. Users will recognize the dashboard, consume the information and – hopefully – act upon it. Think for example about weekly or monthly performance dashboards, or HR dashboards that provide insights in attrition on recurring moments in time.
Dashboards and Storyboards: the “SAP way”
The nuances made above on dashboards and storyboards are being reflected in SAP’s Business Intelligence Suite. Its component Design Studio is a definite managed dashboarding tool. Extremely capable of visualizing insights in a simple and highly attractive way while in the meantime able to have online connections to in-memory data sources, SAP BW or semantic layers. Storyboarding is offered via the on-premise SAP Lumira or via Cloud through the Cloud for Analyticscomponent.
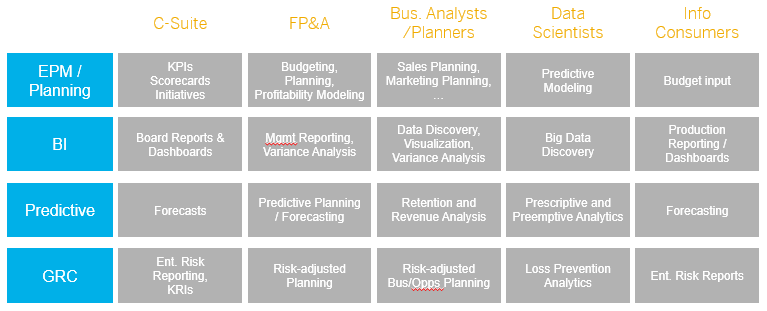
If you have difficulties deciding what to offer to your end users, the BI Componentselection tool I made easily helps you understanding whether your users require dashboards or/and storyboards. You might want to try it.
Financial storyboard
Self-service storyboard created in around 45 minutes using SAP Lumira. On this page the heat-map section that allows for white spot analyses. Data can be exported at any time. User has numerous capabilities to add data, visualizations and additional pages
Financial storyboard
Self-service storyboard created in around 45 minutes using SAP Lumira. User has numerous capabilities to add data, visualizations and additional pages